Full description can be found under Resources
Test Beds
Damper Devices
Multi-Directional Shake Table
Control and Acquisition
A real-time integrated control architecture with software that is identical to that of the Lehigh NHERI Experimental Facility multi-directional real-time hybrid simulation integrated control system, enabling real-time multi-directional shake table hybrid simulations to be performed.

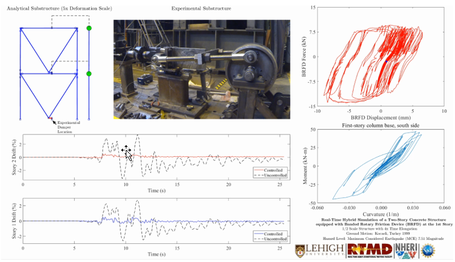
Real-time hybrid simulation of a 2-story reinforced concrete structure with a next-generation rotary friction damper subject to earthquake ground motions scaled to the MCE hazard level.
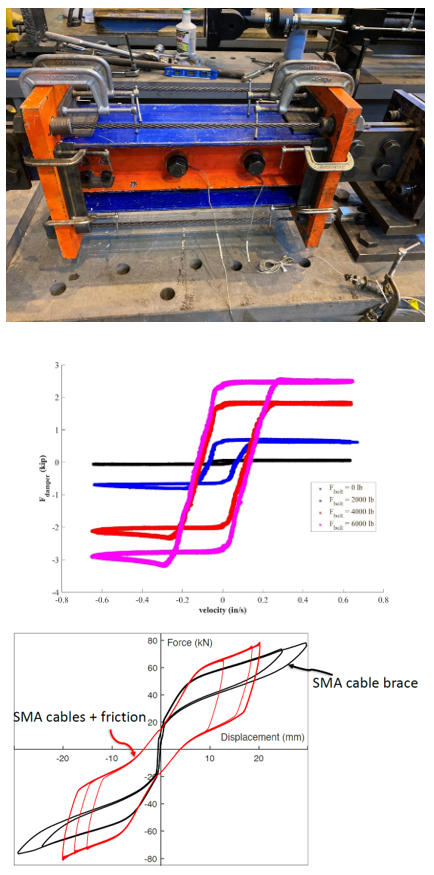
Characterization testing of a shape memory alloy-friction damper
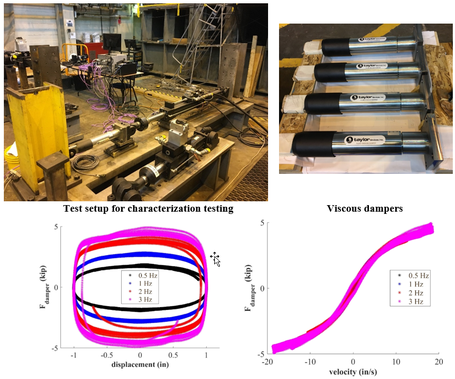
Characterization testing of a nonlinear viscous damper
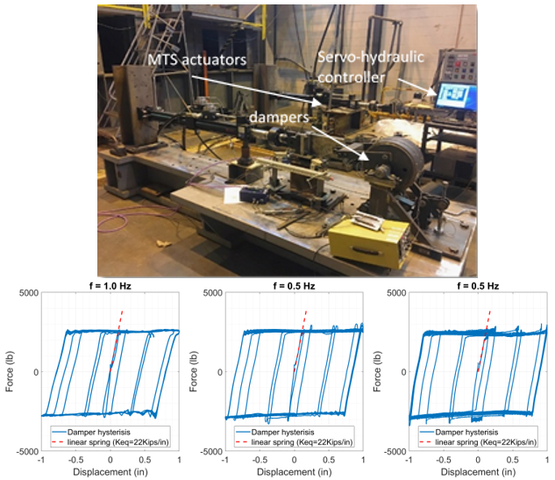
Characterization testing of a next-generation rotary friction damper
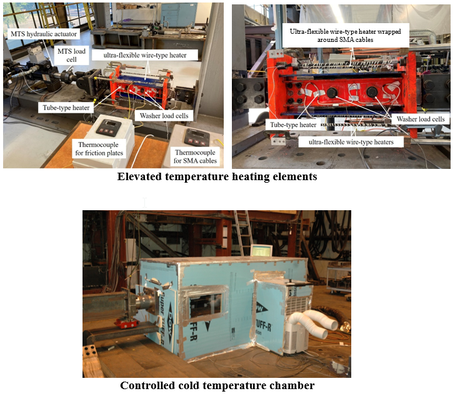
Characterization testing of a shape memory alloy-friction damper at elevated temperatures using heating elements and cold temperature chamber
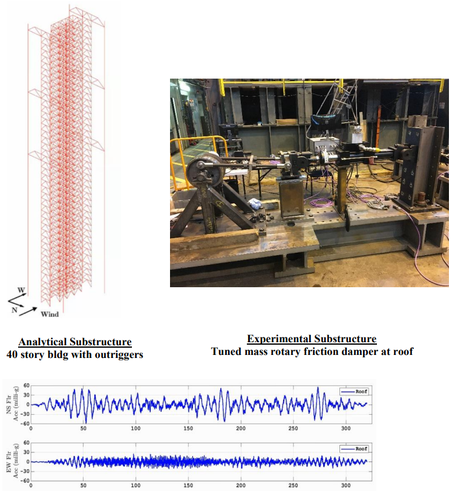
3-D Real-time hybrid simulation of a tall building with tuned mass rotary friction damper subjected to a 700 year MRI 110 mph wind storm.
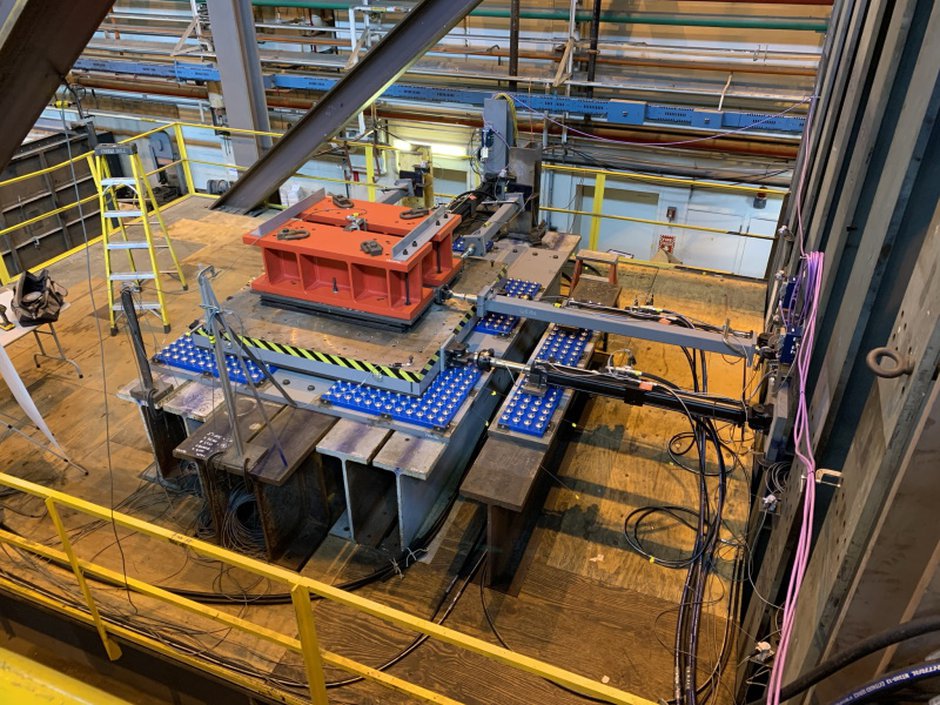

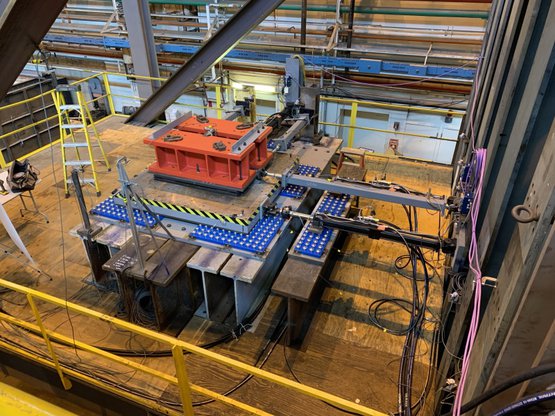
Real-time hybrid simulations of floor isolation systems (RII Track-4:Quantifying Seismic Resilience of Multi-Functional Floor Isolation Systems through Cyber-Physical Testing (OIA 1929151), PI - Scott Harvey, University of Oklahoma)